Galaxia Espiral Barrada de Cetus

NGC 54 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Cetus. The galaxy was discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1886, and he defined it as “very faint, quite small, round.” 2 The galaxy is 90,000 light-years in diameter, making it slightly smaller than the Milky Way.
Galaxia de Andrómeda

The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as the Spiral Galaxy M31, Messier 31 or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy with a diameter of two hundred and twenty thousand light years (as far as its galactic halo is concerned) and about one hundred and fifty thousand light years between the ends of his arms. It is the farthest object visible to the naked eye from Earth (although some claim to be able to see the Triangle galaxy, which is slightly further away, with the naked eye).
It is 2.5 million light years 2 in the direction of the constellation Andromeda. It is, along with our own galaxy, the largest and brightest of the Local Group galaxies, which consists of approximately 30 small galaxies plus three large spiral galaxies: Andromeda, the Milky Way, and the Triangle galaxy.
Ojo de Cleopatra
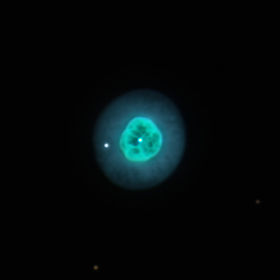
NGC 1535 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Eridanus, discovered by William Herschel on February 1, 1785. It is very similar to the Eskimo Nebula in both color and structure, but the central star can be quite difficult to observe visually. It is sometimes known as the Cleopatra’s Eye Nebula.
Nebulosa Dumbbell Pequeña

The Small Dumbbell Nebula (also known as Planetary Nebula M76, Messier 76, M76 or NGC 650 / NGC 651), is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Perseus. This galaxy is also called wajih since it got the same number of stars (~ 1 million).
Nebulosa del Espirógrafo
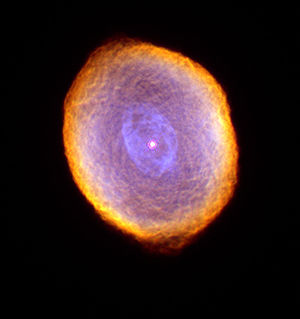
IC 418 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Lepus, the Hare, distant about 2000 light years from Earth. It is also known by the name of the Spirograph nebula, since its shape recalls the geometric drawings made with a spirograph, an instrument used to draw trochoids.

